Traditional finance allows startups to raise funds through specific methods, including but not limited to taking investments from angel investors or VCs, going public through initial public offerings (IPOs), or obtaining loans from the shareholders or accredited institutions. However, blockchain technologies introduced new crowdfunding models, which paved the way for the blockchain startups to raise funds for their projects more easily, in exchange for cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies.
We are happy to announce that we are starting our initial offering series with this post!

In this first post, we will focus on essential differences among the main cryptocurrency-based crowdfunding models, namely Initial Coin Offering (“ICO”), Initial Exchange Offering (“IEO”), and Initial Decentralized Exchange Offering (“IDO”), as follows:
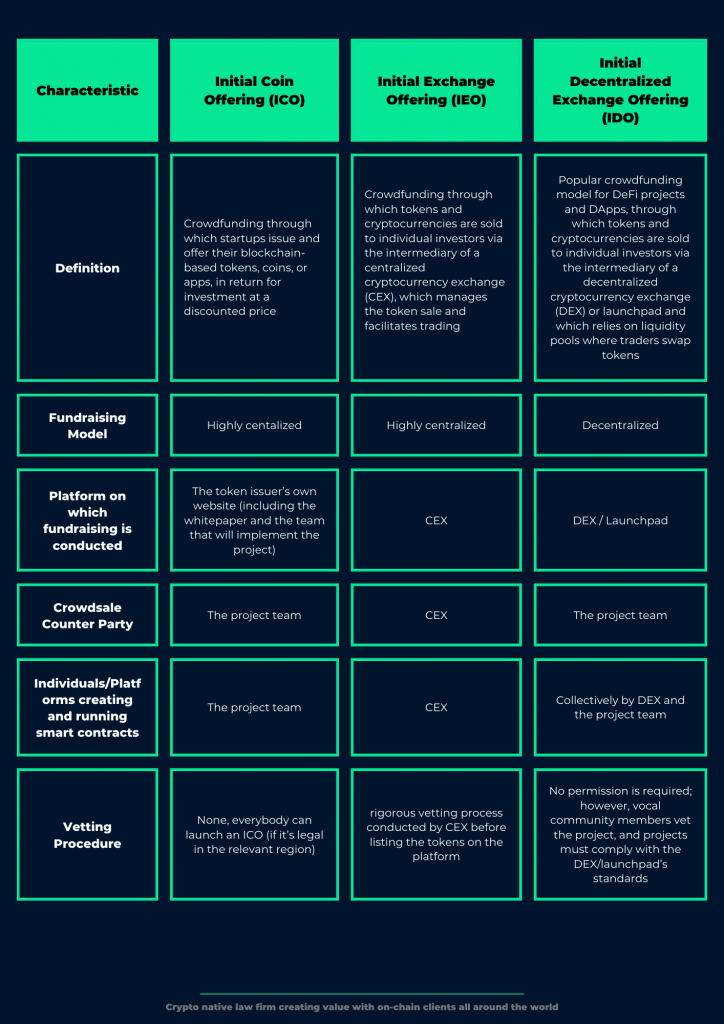
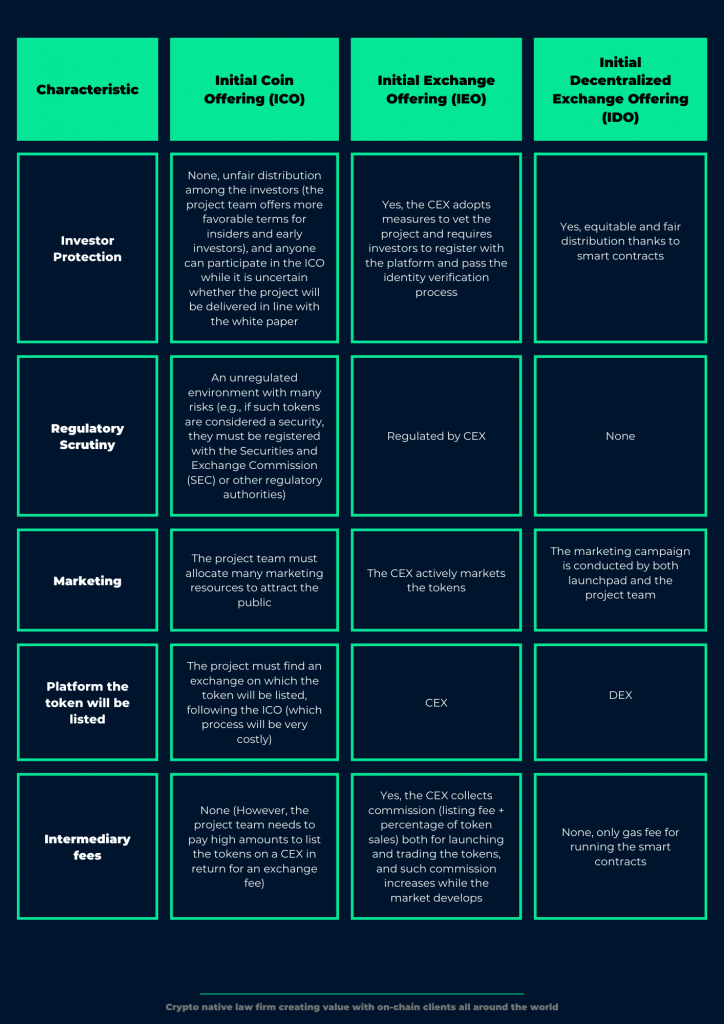

While the foregoing constitutes the main initial offering models, different structures have also been introduced in line with the needs of the blockchain community, such as Security Token Offering (STO),1 Initial Farm Offering (IFO)2 and Initial Game Offering (IGO),3 latters of which are evolved from the IDO structure.
Throughout this series, we will analyze the preceding initial offering models respectively, and in greater detail!
Stay tuned!
Resources,
- Complex and highly regulated crowdfunding model, where tokens are usually equity or asset-backed and represent ownership which is recorded through blockchain.
- One of the recently developed crowdfunding models where investors participate in presale events on a DEX to raise funds for DeFi projects, through the farming feature.
- A crowdfunding model where the investors purchase NFTs and in-game tokens of a blockchain-based game at the early stage in exchange for the launchpad’s native token.